Here you will learn how to configure one-to-one relationships between two entities using Fluent API, if they do not follow EF Core conventions.
Generally, you don't need to configure one-to-one relationships manually because EF Core includes Conventions for One-to-One Relationships. However, if the key or foreign key properties do not follow the convention, then you can use data annotation attributes or Fluent API to configure a one-to-one relationship between the two entities.
Let's configure a one-to-one relationship between the following
Student and StudentAddressentities, which do not follow the foreign key convention.public class Student { public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public StudentAddress Address { get; set; } } public class StudentAddress { public int StudentAddressId { get; set; } public string Address { get; set; } public string City { get; set; } public string State { get; set; } public string Country { get; set; } public int AddressOfStudentId { get; set; } public Student Student { get; set; } }
To configure a one-to-one relationship using Fluent API in EF Core, use the
HasOne, WithOne and HasForeignKey methods, as shown below.public class SchoolContext : DbContext { protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder) { optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer("Server=.\\SQLEXPRESS;Database=EFCore-SchoolDB;Trusted_Connection=True"); } protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder) { modelBuilder.Entity<Student>() .HasOne<StudentAddress>(s => s.Address) .WithOne(ad => ad.Student) .HasForeignKey<StudentAddress>(ad => ad.AddressOfStudentId); } public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; } public DbSet<StudentAddress> StudentAddresses { get; set; } }
In the above example, the following code snippet configures the one-to-one relationship.
modelBuilder.Entity<Student>() .HasOne<StudentAddress>(s => s.Address) .WithOne(ad => ad.Student) .HasForeignKey<StudentAddress>(ad => ad.AddressOfStudentId);
Let's understand it step by step.
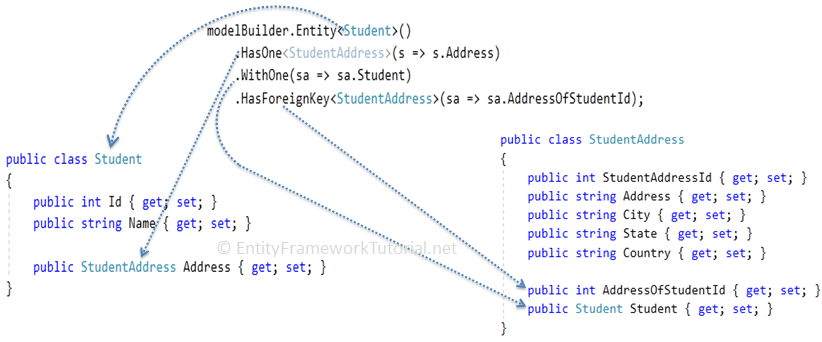
modelBuilder.Entity<Student>()starts configuring theStudententity.- The
.HasOne<StudentAddress>(s => s.Address)method specifies that theStudententity includes oneStudentAddressreference property using a lambda expression. .WithOne(ad => ad.Student)configures the other end of the relationship, theStudentAddressentity. It specifies that theStudentAddressentity includes a reference navigation property ofStudenttype..HasForeignKey<StudentAddress>(ad => ad.AddressOfStudentId)specifies the foreign key property name.
The example above will create the following tables in the database:
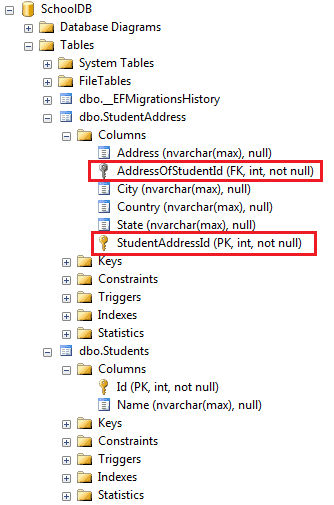
The following figure illustrates the Fluent API configuration for a one-to-one relationship.
You can start configuring with the
StudentAddress entity in the same way, as below.modelBuilder.Entity<StudentAddress>() .HasOne<Student>(ad => ad.Student) .WithOne(s => s.Address) .HasForeignKey<StudentAddress>(ad => ad.StudId);
Thus, you can configure a one-to-one relationship in entity framework core.

No comments:
Post a Comment